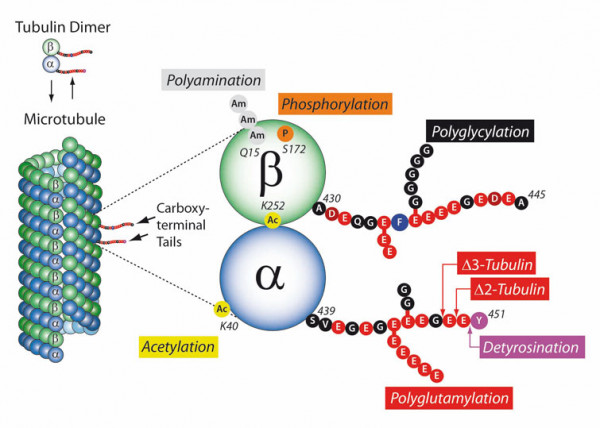
PTMs are highly dynamic and often reversible processes where protein functional properties are altered by the addition of a chemical group or another protein to its amino acid residues. As key cytoskeletal proteins with roles in neuronal development, growth, motility, and intracellular trafficking, tubulins and microtubules (MTs) are major substrates for PTMs. They include tyrosination/detyrosination, α2-tubulin formation, acetylation, phosphorylation, polyamination, ubiquitination, polyglutamylation, and glycylation. Most of these PTMs preferentially take place on tubulin subunits already incorporated into MTs.
The Role of PTMs Is Diverse:
- Tubulin acetylation is generally enriched on stable MTs and acts not by directly stabilizing MTs but rather by affecting the binding of MT inner proteins.
- Detyrosination of the C-terminal tyrosine residue of the α-tubulin protein protects MTs from the depolymerizing activity, thus increasing their longevity.
- Polyglutamylation, which occurs when secondary glutamate side chains are formed on γ-carboxyl groups of glutamate residues, increases during neuronal differentiation. In motile cilia, polyglutamylation regulates beating behavior via the regulation of flagellar dynein motors. Turnover of MTs is stimulated by polyglutamylation via the activation of MT-severing enzymes such as spastin.
- Tubulin polyglycylation generates side chains of glycine residues within the C-terminal tails of α- and β-tubulin. Polyglycylation has a role in stabilizing the axoneme, which is an MT-based cytoskeleton inside cilia and flagella.
MT PTMs generate a "tubulin code" that influences the biological function of the MT cytoskeleton. The readout of this code can be through modulation of higher-order MT structures and/or preferential interactions with selected MT-interacting proteins (MAPs, motors). MTs are involved in biological processes in virtually every cell, tissue, and organ in the body, and MT disturbances underlie many diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's as well as cancer.
Unique Validated PTM-specific Antibodies from AdipoGen Life Sciences
| Antibodies | Clonality | Isotype/Source | Applications |
| Anti-Acetyl-α-Tubulin (Clone TEU318) | Monoclonal | Mouse IgG1 | ICC, WB |
| Anti-Polyglutamylation Modification (Clone GT335) | Monoclonal | Mouse IgG1κ | EM, ICC, IP, WB |
| Anti-Polyglutamylation Modification (Clone GT335) (Biotin) | Monoclonal | Mouse IgG1κ | ICC, IP, WB |
| Anti-Polyglutamate chain (polyE) | Polyclonal | Rabbit | ICC, WB |
Literature
Janke, C. The tubulin code: Molecular components, readout mechanisms, and functions. J.Cell Biol. 206(4), 461-472 (2014).
Photo Credit
Tubulin PTM Overview. Adapted from C. Janke; J. Cell. Biol. 206, 461 (2014)




![Anti-Polyglutamate chain [Poly-E] Anti-Polyglutamate chain [Poly-E]](https://www.biomol.com/media/image/e5/f7/cf/AG-25B-0030-C050_200x200.png)