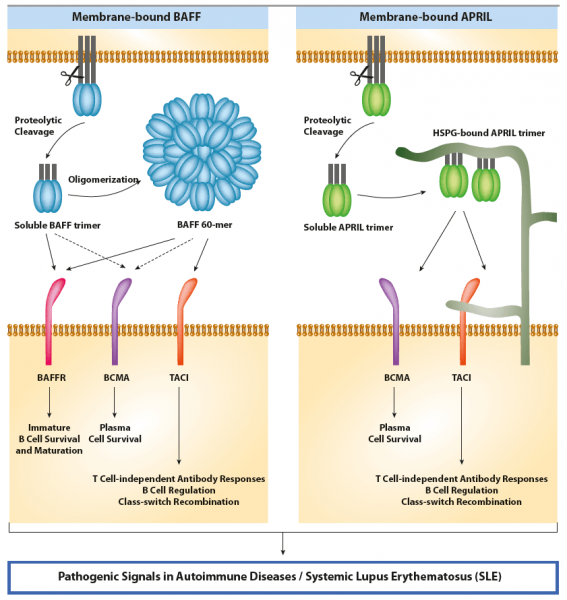
The B cell-stimulating molecules, BAFF (B cell activating factor also known as BLyS; TALL-1; CD257 or TNFSF13B) and APRIL (a proliferation-inducing ligand, also known as CD256 or TNFSF13), are critical factors in the maintenance of the B cell pool and humoral immunity1,2.
APRIL is a secreted protein that binds to transmembrane activator and CAML interactor (TACI), B cell maturation antigen (BCMA) and heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPG). APRIL can interact with carbohydrate side chains of proteoglycans that may trigger cross-linking3.
BAFF is a transmembrane protein which is proteolytically processed by furin to be released as a soluble cytokine2. Soluble BAFF exists either as trimers (BAFF 3-mer), or as an ordered assembly of 20 trimers (BAFF 60-mer)4. BAFF 3-mer and BAFF 60-mer both signal through BAFF-R, only TACI (and BCMA) respond to BAFF 60-mer and not to BAFF 3-mer4. Similar observations are true with APRIL, which needs to be cross-linked in order to activate TACI4.
APRIL maintains B cell homeostasis by acting at a later stage, modulating the function and survival of antigen-experienced B cells. BAFF is a key survival factor for peripheral B cells and together with IL-6 responsible for plasma cell differentiation2. APRIL (as well as BAFF) stimulates class-switch recombination (CSR), hence contributes to shaping humoral effector mechanisms. With regards to humoral memory, APRIL is involved in the establishment and survival of the long-lived plasma cell (LLPC) pool in the bone marrow (BM)5. Besides its major role in B cell biology, BAFF co-stimulates activated T cells.
APRIL is expressed by a number of myeloid-derived cell types including BM granulocytes, megakaryocytes, eosinophils, osteoclasts, and by dendritic cells following exposure to IFN-α, IFN-γ or CD40L. APRIL expression is induced during hematopoiesis in the bone marrow. APRIL expression is not limited to cells of myeloid origin but can be found in epithelial cells of the gut, tonsil, breast and skin. Finally, APRIL is expressed in tumor cell lines and human cancer cells of colon, thyroid and lymphoid origin1.
BAFF is mainly produced by innate immune cells such as neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, follicular dendritic cells, T cells, activated B cells, some malignant B cells, but non-lymphoid cells like astrocytes, synoviocytes and epithelial cells can also produce BAFF.
BAFF and APRIL are implicated in several human autoimmune diseases with autoreactive B cell involvement, including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)6, Sjö gren’s syndrome (SS)7, IgA nephropathy (IgAN)8, and rheumatoid arthritis (RA)9. APRIL might also function in enhancing proliferation of some tumor cells, especially B cell malignancies10,11. BAFF levels are also increased in some lymphoid cancers12.
APRIL & BAFF ELISA Kits
APRIL (human) ELISA Kit - The BEST on the Market!
The APRIL (human) ELISA Kit (Item No. AG-45B-0012-KI01) is a sandwich ELISA for specific quantitative determination of human APRIL in serum, plasma and cell culture supernatants. This ELISA Kit shows both high specificity and high sensitivity, which is a clear advantage compared to other APRIL (human) ELISA Kits from key competitors.
- Sensitivity: 7 pg/ml
- Range: 7.8 to 500 pg/ml
- Sample: Cell Culture Supernatant, Plasma, Serum
- Specificity: Serum from a healthy patient is left untreated or treated with 1 μg/ml of the APRIL receptor, TACI (human):Fc (human) (Item No. AG-40B-0079). APRIL levels were measured using the APRIL (human) ELISA Kit (Item No. AG-45B-0012-KI01)

BAFF, Soluble (human) ELISA Kit (hypersensitive) - The RELIABLE Assay
The BAFF, Soluble (human) ELISA Kit (Item No. AG-45B-0001-KI01) is a sandwich ELISA for specific quantitative determination of human BAFF in serum, plasma and cell culture supernatants. This ELISA Kit does not cross-react with mouse BAFF and has been chosen by several CROs for its high specificity and high sensitivity
- Sensitivity: 8 pg/ml
- Range: 15.6 to 500 pg/ml
- Sample: Cell Culture Supernatant, Plasma, Serum
- Specificity: Serum from a healthy patient or patient with multiple sclerosis is left untreated or treated with 0.5 μg/ml of a BAFF receptor, TACI (human):Fc (human) (AG-40B-0079). BAFF levels are measured using the BAFF, Soluble (human) ELISA Kit (hypersensitive) (AG-45B-0001-KI01).

References
- Targeting BAFF and APRIL in systemic lupus erythematosus and other antibody-associated diseases: E. Samy, et al.; Int. Rev. Immunol. 36, 3 (2017)
- Cracking the BAFF code: F. Mackay & P. Schneider; Nat. Rev. Immunol. 9, 491 (2009)
- Identification of proteoglycans as the APRIL-specific binding partners: K. Ingold, et al.; J. Exp. Med. 201, 1375 (2005)
- TACI, unlike BAFF-R, is solely activated by oligomeric BAFF and APRIL to support survival of activated B cells and plasmablasts: C. Bossen, et al.; Blood 111, 1004 (2009)
- Factors of the bone marrow microniche that support human plasma cell survival and immunoglobulin secretion: D.C. Nguyen, et al.; Nat. Commun. 12, 3698 (2018)
- Raised serum APRIL levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: T. Koyama, et al.; Ann. Rheum. Dis. 64, 1065 (2005)
- The expression of APRIL in Sjogren’s syndrome: Aberrant expression of APRIL in the salivary gland: J.L. Vosters, et al.; Rheumatology (Oxford) 51, 1557 (2012)
- Increased APRIL Expression Induces IgA1 Aberrant Glycosylation in IgA Nephropathy: Y.L. Zhai, et al.; Medicine (Baltimore) 95, e3099 (2016)
- The BAFF/APRIL system: an important player in systemic rheumatic diseases: F. Mackay, et al.; Curr. Dir. Autoimmun. 8, 243 (2005)
- APRIL, a New Ligand of the Tumor Necrosis Factor Family, Stimulates Tumor Cell Growth: M. Hahne, et al.; J. Exp. Med. 188, 1185 (1998)
- In situ detection of APRIL-rich niches for plasma-cell survival and their contribution to B-cell lymphoma development: M. Burjanadze, et al.; Histol. Histopathol. 24, 1061 (2009)
- Serum BAFF predicts prognosis better than APRIL in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with rituximab plus CHOP chemotherapy: S.J. Kim, et al.; Eur. J. Haematol. 81, 177 (2008)