Cookie preferences
This website uses cookies, which are necessary for the technical operation of the website and are always set. Other cookies, which increase the comfort when using this website, are used for direct advertising or to facilitate interaction with other websites and social networks, are only set with your consent.
Configuration
Technically required
These cookies are necessary for the basic functions of the shop.
"Allow all cookies" cookie
"Decline all cookies" cookie
CSRF token
Cookie preferences
Currency change
Customer-specific caching
FACT-Finder tracking
Individual prices
Selected shop
Session
Comfort functions
These cookies are used to make the shopping experience even more appealing, for example for the recognition of the visitor.
Note
Show the facebook fanpage in the right blod sidebar
Statistics & Tracking
Affiliate program
Conversion and usertracking via Google Tag Manager
Track device being used
| Item number | Size | Datasheet | Manual | SDS | Delivery time | Quantity | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cay32011-100 | 100 µg | - |
6 - 10 business days* |
439.00€
|
If you have any questions, please use our Contact Form.
You can also order by e-mail: info@biomol.com
Larger quantity required? Request bulk
You can also order by e-mail: info@biomol.com
Larger quantity required? Request bulk
TIM-3 is a member of the T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain containing (TIM) protein family... more
Product information "TIM-3 Extracellular Domain (human, recombinant)"
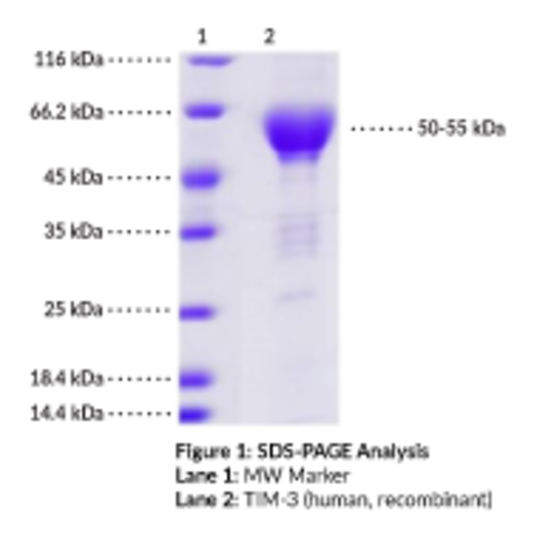
TIM-3 is a member of the T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain containing (TIM) protein family of immunoregulatory proteins and is encoded by the HAVCR2 gene in humans. It is a transmembrane protein composed of an N-terminal immunoglobulin variable (IgV) domain, as well as mucin stalk, transmembrane, and C-terminal cytoplasmic tail domains. The IgV domain contains cysteine residues that form non-canonical intramolecular disulfide bonds resulting in a cleft and channel not found in non-TIM immunoglobulin domains that is important for non-canonical ligand binding. TIM-3 is expressed primarily on T cells but is also expressed on other immune cells such as natural killer and dendritic cells. The TIM-3 ligand galectin 9 (Cay-32012), located on immune or tumor cells, binds to glycosylated sites of the IgV and mucin stalk domains and induces TIM-3 oligomerization to activate downstream signaling that impairs immune synapse formation and leads to T cell anergy or apoptosis. The TIM-3 IgV cleft domain binds non-canonical ligands, such as phosphatidylserine on apoptotic cells or CEACAM1 on antigen-presenting or tumor cells. TIM-3 is an inhibitory co-receptor that helps maintain immune tolerance but, when expressed on certain cells during chronic infection or cancer, can lead to immune exacerbation. Inhibition of the TIM-3 pathway by Tim-3 fusion or extracellular domain-only proteins prevents the induction of immune tolerance in a mouse islet allograft model or increases weight loss and tissue injury in a mouse model of TNBS-induced colitis, respectively. Expression of TIM-3 is decreased in patients with autoimmune diseases, including ulcerative colitis. TIM-3 is expressed on tumor-infiltrating T cells and expressed on a higher proportion of regulatory T cells from cancer patients. Its overexpression on T cells increases tumor progression in an EL4 mouse model of lymphoma, while TIM-3 inhibition decreases tumor growth in a mouse model of head and neck cancer. SNPs in HAVCR2 are associated with allergic diseases, immunity, and cancer. Cayman's TIM-3 Extracellular Domain (human, recombinant) protein is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer, comprised of TIM-3 (amino acids 22-200) fused to mouse IgG1 Fc at its C-terminus, consists of 412 amino acids, has a calculated molecular weight of 46.2 kDa, and a predicted N-terminus of Ser22 after signal peptide cleavage. As a result of glycosylation, the monomer migrates at approximately 50-55 kDa by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions.Synonyms: CD366, Hepatitis A Virus Cellular Receptor 2 Precursor, KIM-3, T Cell Immunoglobulin and Mucin Domain-containing Protein 3, T Cell Immunoglobulin Mucin Receptor 3, T Cell Membrane Protein 3, TIMD-3. Purity: >90% estimated by SDS-PAGE. Source: Recombinant C-terminal mouse IgG2a Fc-tagged TIM-3 expressed in HEK293 cells. Amino Acids: 22-200. MW: 46.2 kDa. Formulation: (Request formulation change), Lyophilized from sterile 20 mM Tris, 150 mM sodium chloride, pH 8.5.
| Keywords: | CD366, Hepatitis A Virus Cellular Receptor 2 Precursor, KIM-3, TIMD3 |
| Supplier: | Cayman Chemical |
| Supplier-Nr: | 32011 |
Properties
| Conjugate: | No |
| Host: | Human cells |
| Species reactivity: | human |
| MW: | 46.2 kD |
| Purity: | >90% estimated by SDS-PAGE |
| Format: | Lyophilized |
Database Information
| KEGG ID : | K20414 | Matching products |
| UniProt ID : | Q8VIM0 | Matching products |
| Gene ID | GeneID 171285 | Matching products |
Handling & Safety
| Storage: | -80°C |
| Shipping: | -80°C (International: -80°C) |
Caution
Our products are for laboratory research use only: Not for administration to humans!
Our products are for laboratory research use only: Not for administration to humans!
Information about the product reference will follow.
more
You will get a certificate here
Viewed



