Cookie-Einstellungen
Diese Website benutzt Cookies, die für den technischen Betrieb der Website erforderlich sind und stets gesetzt werden. Andere Cookies, die den Komfort bei Benutzung dieser Website erhöhen, der Direktwerbung dienen oder die Interaktion mit anderen Websites und sozialen Netzwerken vereinfachen sollen, werden nur mit Ihrer Zustimmung gesetzt.
Konfiguration
Technisch erforderlich
Diese Cookies sind für die Grundfunktionen des Shops notwendig.
"Alle Cookies ablehnen" Cookie
"Alle Cookies annehmen" Cookie
Ausgewählter Shop
CSRF-Token
Cookie-Einstellungen
FACT-Finder Tracking
Individuelle Preise
Kundenspezifisches Caching
Session
Währungswechsel
Komfortfunktionen
Diese Cookies werden genutzt um das Einkaufserlebnis noch ansprechender zu gestalten, beispielsweise für die Wiedererkennung des Besuchers.
Facebook-Seite in der rechten Blog - Sidebar anzeigen
Merkzettel
Statistik & Tracking
Endgeräteerkennung
Kauf- und Surfverhalten mit Google Tag Manager
Partnerprogramm
NEU
Bei Fragen nutzen Sie gerne unser Kontaktformular.
Bestellen Sie auch per E-Mail: info@biomol.com
Größere Menge gewünscht? Bulk-Anfrage
Bestellen Sie auch per E-Mail: info@biomol.com
Größere Menge gewünscht? Bulk-Anfrage
Organism: Homo sapiens (Human). Source: E.coli. Expression Region: 122-199aa. Protein Length:... mehr
Produktinformationen "Double-stranded RNA-specific adenosine deaminase (ADAR), partial, human, recombinant"
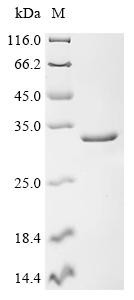
Organism: Homo sapiens (Human). Source: E.coli. Expression Region: 122-199aa. Protein Length: Partial. Tag Info: N-terminal GST-tagged. Target Protein Sequence: GVDCLSSHFQ ELSIYQDQEQ RILKFLEELG EGKATTAHDL SGKLGTPKKE INRVLYSLAK KGKLQKEAGT PPLWKIAV. Purity: Greater than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE. Endotoxin: Not test. Biological Activity: n/a. Form: Liquid or Lyophilized powder. Buffer: If the delivery form is liquid, the default storage buffer is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 5%-50% glycerol. If the delivery form is lyophilized powder, the buffer before lyophilization is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose, pH 8.0. Reconstitution: We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20 °C/-80 °C. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference. Storage: The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself. Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20 °C/-80 °C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20 °C/-80 °C. Notes: Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4 °C for up to one week. Relevance: Catalyzes the hydrolytic deamination of adenosine to inosine in double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) referred to as A-to-I RNA editing. This may affect gene expression and function in a number of ways that include mRNA translation by changing codons and hence the amino acid sequence of proteins since the translational machinery read the inosine as a guanosine, pre-mRNA splicing by altering splice site recognition sequences, RNA stability by changing sequences involved in nuclease recognition, genetic stability in the case of RNA virus genomes by changing sequences during viral RNA replication, and RNA structure-dependent activities such as microRNA production or targeting or protein-RNA interactions. Can edit both viral and cellular RNAs and can edit RNAs at multiple sites (hyper-editing) or at specific sites (site-specific editing). Its cellular RNA substrates include: bladder cancer-associated protein (BLCAP), neurotransmitter receptors for glutamate (GRIA2) and serotonin (HTR2C) and GABA receptor (GABRA3). Site-specific RNA editing of transcripts encoding these proteins results in amino acid substitutions which consequently alters their functional activities. Exhibits low-level editing at the GRIA2 Q/R site, but edits efficiently at the R/G site and HOTSPOT1. Its viral RNA substrates include: hepatitis C virus (HCV), vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), measles virus (MV), hepatitis delta virus (HDV), and human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). Exhibits either a proviral (HDV, MV, VSV and HIV-1) or an antiviral effect (HCV) and this can be editing-dependent (HDV and HCV), editing-independent (VSV and MV) or both (HIV-1). Impairs HCV replication via RNA editing at multiple sites. Enhances the replication of MV, VSV and HIV-1 through an editing-independent mechanism via suppression of EIF2AK2/PKR activation and function. Stimulates both the release and infectivity of HIV-1 viral particles by an editing-dependent mechanism where it associates with viral RNAs and edits adenosines in the 5'UTR and the Rev and Tat coding sequence. Can enhance viral replication of HDV via A-to-I editing at a site designated as amber/W, thereby changing an UAG amber stop codon to an UIG tryptophan (W) codon that permits synthesis of the large delta antigen (L-HDAg) which has a key role in the assembly of viral particles. However, high levels of ADAR1 inhibit HDV replication. Reference: Molecular cloning of cDNA for double-stranded RNA adenosine deaminase, a candidate enzyme for nuclear RNA editing.Kim U., Wang Y., Sanford T., Zeng Y., Nishikura K.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91:11457-11461(1994). Function: nan
| Schlagworte: | ADAR, p136, DRADA, ADAR1, IFI-4, K88DSRBP, Interferon-inducible protein 4, 136 kDa double-stranded RNA-binding protein, Double-stranded RNA-specific adenosine deaminase, Recombinant Human Double-stranded RNA-specific adenosine deaminase (ADAR), partial |
| Hersteller: | Cusabio |
| Hersteller-Nr: | EP001324HU2 |
Eigenschaften
| Anwendung: | Activity not tested |
| Konjugat: | No |
| Wirt: | E.coli |
| Spezies-Reaktivität: | human |
| MW: | 35.0 kD |
| Reinheit: | >85% (SDS-PAGE) |
Datenbank Information
| KEGG ID : | K12968 | Passende Produkte |
| UniProt ID : | P55265 | Passende Produkte |
| Gene ID | GeneID 103 | Passende Produkte |
Handhabung & Sicherheit
| Lagerung: | -20°C |
| Versand: | +4°C (International: +4°C) |
Achtung
Nur für Forschungszwecke und Laboruntersuchungen: Nicht für die Anwendung im oder am Menschen!
Nur für Forschungszwecke und Laboruntersuchungen: Nicht für die Anwendung im oder am Menschen!
Hier kriegen Sie ein Zertifikat
Loggen Sie sich ein oder registrieren Sie sich, um Analysenzertifikate anzufordern.
Bewertungen lesen, schreiben und diskutieren... mehr
Kundenbewertungen für "Double-stranded RNA-specific adenosine deaminase (ADAR), partial, human, recombinant"
Bewertung schreiben
Loggen Sie sich ein oder registrieren Sie sich, um eine Produktbewertung abzugeben.
Zuletzt angesehen


